Common hreflang attribute errors
1. Invalid format. The language code is indicated first, and then the region code is specified. To determine the code, you need to use the language ISO 639-1 and the regional ISO 3166-1 Alpha 2 standards. Before implementing an attribute, it is important to verify that the link format complies with the specified standards.
For example, you need to create a page for English-speaking citizens living in the United States. Using the "en-us" format is correct. For English-speaking citizens from the UK, the correct sequence is "en-gb," but not "en-uk." According to the rules of setting the attribute, the language must be specified, and the region may be completely absent.
In some links, only the region is found, and this is wrong. It is allowed to use the only language so that the page is displayed to people who speak a specific language, but are located anywhere in the world.
2. Separation of language and region using dashes or underscores. The only correct option is to use a hyphen. For example, "en-us" is correct, and "fr_uk" is incorrect.
3. Conflicts in the attribute code. Setting up hreflang involves using a single page for one language. In other words, one language version corresponds to a single URL in the code. Multiple pages cannot be written in one language.
In the example, the English version is used for all pages. This is an error:
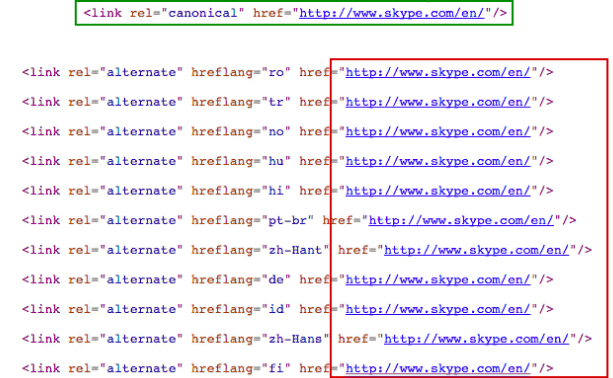
4. Typos. For example, instead of "fr" which stands for France, "fi" is used which means Finland. However, the page content is written in French. This page will not be indexed by the search engine. To avoid such errors, use the hreflang tag generator .
5. Hreflang attributes with errors in links:
links direct to pages that do not exist. When clicking on the URL, an error 4xx or 5xx is shown;
lacking a specific hreflang element. If a language version exists, but no attribute has been created for it;
the ones redirect to another page. In this case, the second URL is not indexed;
without full indication of their components. We are talking about the so-called relative links with the missing first part Incorrect: /catalog1/file1.html Correct: http://site.com/catalog1/file1.html 6. Lack of backlinks. Problems with hreflang occur in the absence of return confirmative links to the attribute. If page 1 refers to page 2, then page 2 must have a backlink to page 1.
Any of these errors on a specific page leads to the fact that it will not be indexed by a search engine robot.
How to find and fix hreflang errors
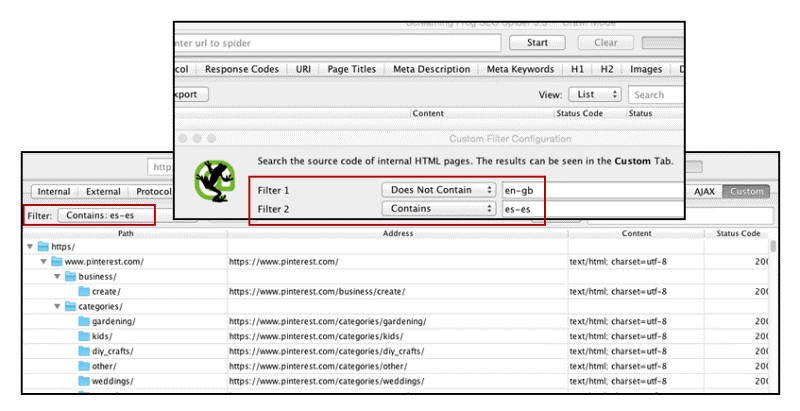
You will have to revise the hreflang attribute code yourself to detect errors in writing letters and hyphens and check the correspondence of languages and regions. Use the Screaming Frog service to determine the mismatch of one language version to a single page:
What you need to do to prevent errors:
1. Use absolute links instead of relative ones.
2. Each time you add the hreflang attribute, check the data for compliance with the standards.
3. Delete URLs displaying 4xx or 5xx error codes and redirect pages.
4. Determine what is more important for the website: user language or region. In the first case, do not use the location indication, and specify the language and country in the second one.
Conclusion
The problems with the hreflang attribute are mainly caused by:
errors in specifying languages and regions according to the standards;
using nonexistent links and redirects;
lack of backlinks to pages with the attribute;
the order of specifying the component links with the hreflang attribute;
specifying multiple pages for one language version.
To find the hreflang attributes with errors and fix them, you need to conduct a small audit of the pages and adjust everything that does not comply with the rules for setting up sites with several language versions.
