What are lang and hreflang attributes
If the company operates in different countries and has a multilingual resource, it should be pointed, using special attributes, for which region and language some page is intended. As a result, the search engines may identify various versions of the site and provide users with the right variant.
Besides, these attributes help to avoid problems with Content Duplication, which may be a reason for pages indexing with similar content for a variety of regions.
For example, in the international on-line shop there will be the same descriptions of goods, however, the currency will differ for Great Britain and the USA. If you do not indicate the separate region for every page version, search systems can consider them duplicates.
Google recommends pointing out language and regional versions for multilingual sites for the following cases:
- Only menu items and information at the bottom of the page are translated, and the basic information is in the main language. This option is most frequently used for sections with user content - on forums or feedback pages.
- The site has one language with some regional differences. For instance, the English content is a little different for people from the USA, New Zealand, and Australia.
- All project pages are in different languages. As an example, resource in Italian was translated into French and Spanish.
For specific geographic areas you can mark alternate pages versions in different languages by these ways:
- by means of hreflang attribute HTML tag <link>
- by adding versions in HTTP headers:
- in the sitemap.xml file:

- by adding <lang> attribute in the <html> tag:

Rules for specifying languages and pages regions
- Tags will be considered by search systems if all language pages have reciprocal links. At the same time, every page variation must have his own hyperlink ;
- it is necessary to indicate complete addresses, starting with HTTP or HTTPS;
- page versions can be hosted on different domains;
- hreflang attribute may contain the information only about language code or completed with region data, for which a specific page is created;
- it is expected, what version will be displayed for the user, whose browser settings has language different from the presented resource. For example, a user who speaks Chinese is more likely to understand the page in English than in Ukrainian.
To indicate a default page, it can be used the optional value x-default with the following syntax:
<link rel="alternate" href="https://site.com/" hreflang="x-default" />
This parameter is used in the following cases:
- if the project has IP-dependent pages, from which users are served to the appropriate language version of the site;
- for pages, having the possibility of dynamic content choice on some languages;
- for pages where there are a language and region selections.
How to use hreflang in <link> tag
Attribute hreflang is added to the section heading <head> and has the following syntax:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="language code" href="URL-address" >
For instance, the syntax defining three alternative site versions on English, Ukrainian and Russian will be the following:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en" href="https://mysite.com/" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="uk" href="https://mysite.com/uk/" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="ru" href="https://mysite.com/ru/" />
Links to all versions, including the home page are added to the header.
Google cannot recognize an appropriate language for the visitor based on the URL; it is important to indicate its code explicitly. In this case, users from Russia, Ukraine, and England or visitors, speaking of these languages, reach necessary landing pages from search results. The information about the region and language of the user is defined by browser settings.
This way can be rather cumbersome for sites, which are translated into many languages. Adding a long code with all links negatively affects the performance of the project. Therefore, for such major projects, it may be preferable to use other ways of indicating the languages.
Using hreflang in HTTP headers
The informing search systems about page versions in different languages and optimized for certain regions can be with using HTTP headers. This is the preferable option for file optimization, which created not in HTML-format, but, for example, in terms of PDF-documents and other content.
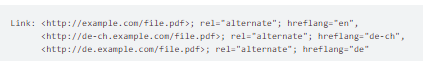
The information in headers is written in the following way:
Link: <full URL of file on the first language>; rel="alternate"; hreflang="two-letter code of the first language", <full URL of file on the second language>; rel="alternate"; hreflang="two-letter code of the second language"
Adding hreflang to Sitemap
Besides, it can be used to indicate language and regional versions of Sitemap pages. The list of necessary links is added to this file as follows:
- Firstly, it is necessary to write namespace correctly.
- Then to add <URL> tag.
- After it follows <loc> tag, which has the URL of the page.
- Then all versions with homepage are specified together in <xhtml:link> tag, where language and region codes are indicated.
- </URL> closing tag is placed.
- After that, items 2-5 are repeated for all URLs with existing language versions.
Using lang attribute in <html> tag
An alternative method to inform a search system about the language of the page is to add lang in <html> tag. This attribute specifies the language for the whole page, including its title. If text passages in other languages are placed on the page, for them can be specified necessary meaning different from the set in <html> tag.
The example of syntax to set English language:
<html lang="en">
In order to set a certain language dialect, it is necessary to use BCP 47 specification coding. For example, es-419 code denotes Spanish used in Latin America and the Caribbean locations. In order to figure out the necessary codes, you can use the Language Subtag Lookup utility, which has access to a list of all language codes filtered by certain parameters:
Validation of multilingual project version
To check the correctness of typed language and regional data on the site, it is possible by using Flang validator, indicating the URL of the project and clicking "Validate now!".
There is also another validator - hreflang.ninja , which works in the same way.
Conclusion
- The setting of language and region on the pages of multilingual sites and projects will help visitors to go on relevant pages in search results.
- Thanks to using lang and hreflang attributes, there is not just an improvement of user experience but also the exception of the problem of content duplication, which is important to SEO. Search systems even recognize pages with similar content as adapted to different regions.
- Using hreflang x-default allows providing a universal page version. Users, living in countries and speaking languages, which are not defined on the site by hreflang, will be served on this page.
- Specifying language, regional, and dialect codes, it is important to check their compliance with the specifications. It can be checked by offered above validators.
