Besides, the desire to figure out the SEO nuances often leads to a total misunderstanding of what should be done.
I am going to strip away the most common myths about the optimization of Title, Description and Alt meta-tags in this article. My task is also to develop comprehensive instruction based on official sources to help you adjust these tags. Also, I will suggest a way to make descriptions and H-titles and give you some practical examples that will help you out with page optimization.
Meta-tags and image optimization in official sources
Let's see what purposes metadata, H1-H6 headings and ALT attributes serve for. I suggest referring to the following webmaster manuals:
The chapter about indexing in Google manual for webmasters includes the following warning:
Make sure that <title> elements and <alt> attributes are informative and do not contain any mistakes.
And in <metatags> section we find this:
Webmasters can provide search engines with information about their web sites with the help of meta tags, Various systems use meta-tags, but each system has its own type. Meta tags are added to the <head> section of an HTML page.
ALT attribute detailed explanation can be found here .
<Alt> attribute serves to describe a graphic file. There are several reasons why it is so important. The description provides Google with useful data regarding the subject of the image. Thus, it lets us use this info to define the most relevant pictures on user request.
This article describes each kind of meta-tags and image optimization. To give a brief review:
While indexing your website, a search robot sees your page as an HTML document. To indicate any important data, we use specific tags. The data may contain search queries (keywords), so it gives us an opportunity to optimize meta-tags. Besides, keeping in mind that search engines treat web pages as text, we need to make up related phrases for every picture on the page so that the robot could find them. We should use ALT attribute for this purpose. One more step is necessary to be done - to optimize image links and the relating text beside them.
However, these tags are often used in a wrong way and for incorrect purposes, so let us discuss the common myths.
Myths concerning meta-tags optimization
Myth #1
The matter of Title and Description tags size
One of the most common myths concerning the size of Title and Description is that the number of symbols in these tags is strictly defined. Most SEO audit services often make such warnings.
Put in perspective these recommendations. Treat them as relative guidance but not a sustainable axiom.
Google Search Console checks these parameters the same way as the resource self-descriptiveness:
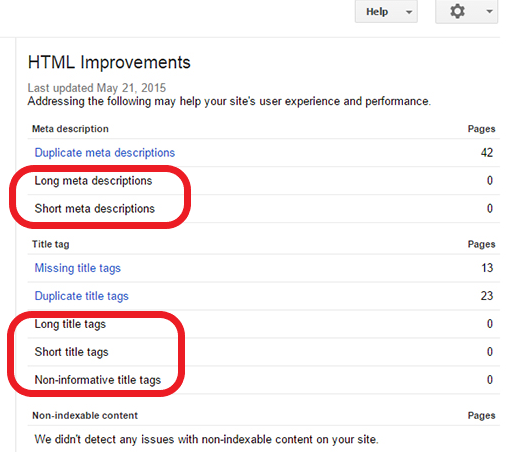
Why is the number of words in Title so important
Title and Description are involved in snippet formation, that is why it would be logical to adjust the number of characters so that they all could fit into search results. However, the snippet is formed at the discretion of a search engine and at the same time depends on the query used.
A search system can compose snippets itself using the content of the found pages, <title> and <description> tags, schema markup data, XML files and website descriptions in DMOZ. The snippet content also depends on a user request. That is why different snippets can be formed for one and the same page. You can influence snippets content through texts changing procedure in the data sources mentioned above.
Therefore, our efforts and calculations might fail to work. Moreover, the actions taken can be harmful.

The main requirement for meta-tags is "to make them informative". But how can one make informative meta-tags for a web page which sells "Components for solar panels"? Or how should one change a short title of "Contacts" page?
Well, there is no need to do it. Stay a consecutive thinker and don't make title size too long or short without any necessity.
Myth #2
Title + Description = Snippet
That topic has been already touched on in the previous chapter. There is a strong belief that Title and Description are the core components of a snippet, but actually, they are not. Despite the fact that Title and Description get into the snippet, it doesn't always happen exactly this way.
Let's compare the snippets of one and the same query:
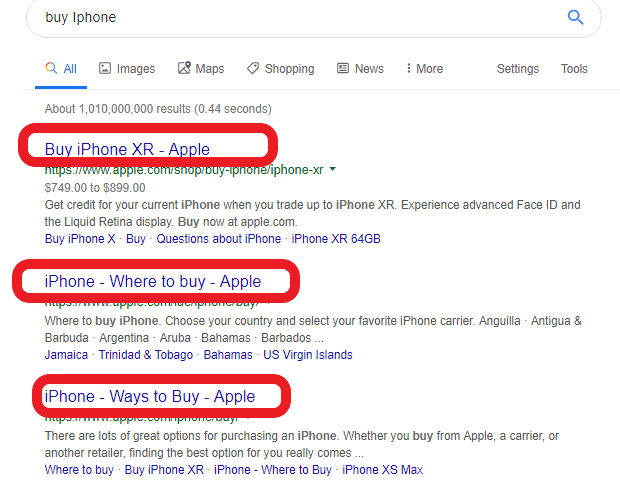
We see that the snippets of these pages are different. And yes, the title remains, but it can also vary according to the user request. The myth stating that meta-tags equals to snippet is quite irrational and even dangerous. Attempting to compose a good description, you might fail to use the possibilities that meta-tags enable us in the context of optimization.
If you wish to see the "wonderful" snippet examples, go to the third page of search results. Try it with the same " Buy iPhone USA" query:
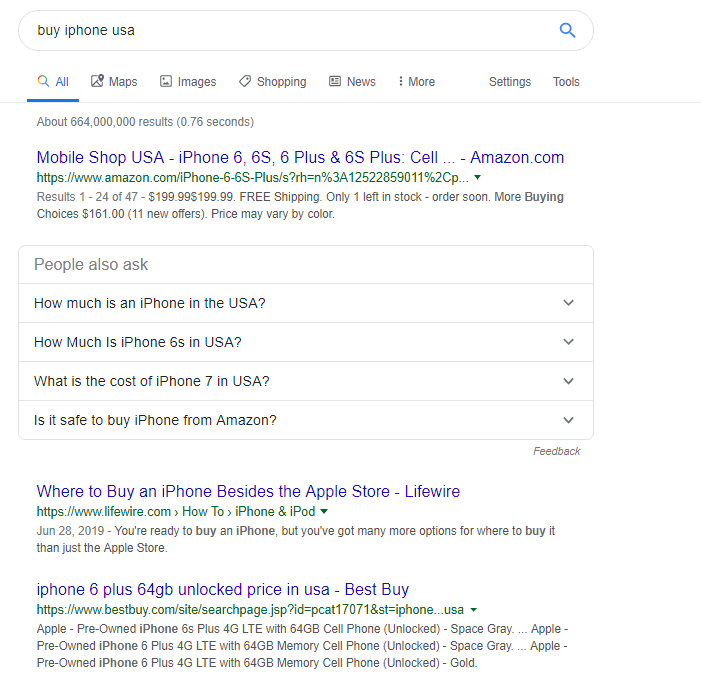
Myth #3
Use of irrelevant words on the page
I am referring to writing anything that may be "useful" into meta-tags and tags for image optimization. The reason I include it into myths is the following: if an SEO-specialist does anything like this, then he either does it on purpose (to test a theory, for example), or it simply means that he cannot be a specialist.
Website owners often follow the showcase concept - to display all the best products at a time.
So what we get is the titles like this one:
"Spanners, lawnmowers, impact wrenches, chainsaws, boilers and radiators in our catalog."
Here is a bad example given by Google:
<img src="puppy.jpg" alt="puppy dog doggy small dog baby dog fluffy little puppies pionter jack russel spaniel terrier retriever dog food cheap dog food food for puppies low price dog food wet dog food dog treats"/>
Filling up ALT tag with keywords ("irrelevant keywords") is the shortest way to create a user's negative opinion, so your site will be considered spam. Attempt to create the content that is highly informative and contain relating keywords that correlate with the context.
Don't forget, that relevance is evaluated coordinating a query and a page, so don't use a wrong strategy that won't do any good.
SEO is about attracting clients with a ready demand implied in "keywords". Selling a boiler to the one who came for a spanner is not appropriate.
Myth #4
A keyword in metadata equals to "top"
I'm sure most SEO-masters recall these discussions:
- "This product makes 50% of our income, include it into the title".
- Actually it sounds like: "You deleted this word from the title and now we've got no positions".
- And a sophisticated variant: "Include the word "exclusive" into all titles, because that's what we sell".
Metadata is the information that is provided for search engines, but you are wrong if you think that a keyword used in these tags gets your site to strike the top.
Webpage optimization is a complex of means. There are many sites that use metadata according to existing standards, but a complex approach to a range of factors lets them take top positions in search results.
Requirements for efficient meta-tags and images optimizing process
There are some strict requirements for meta-tags and image optimization. To define them, we should turn to the official tools that search engines use. The requirements can be divided into two groups:
- The ones that are set up in search engines tools;
- Other ones that come naturally if we think logically according to the instructions given above.
What do the official tools record
#1
Metadata doubles
Google Search Console webmaster in the chapter "HTML optimization" provides a report on duplicate meta descriptions in terms of optimization. Web pages that contain double meta descriptions and double content are not likely to appear in top positions of search results.
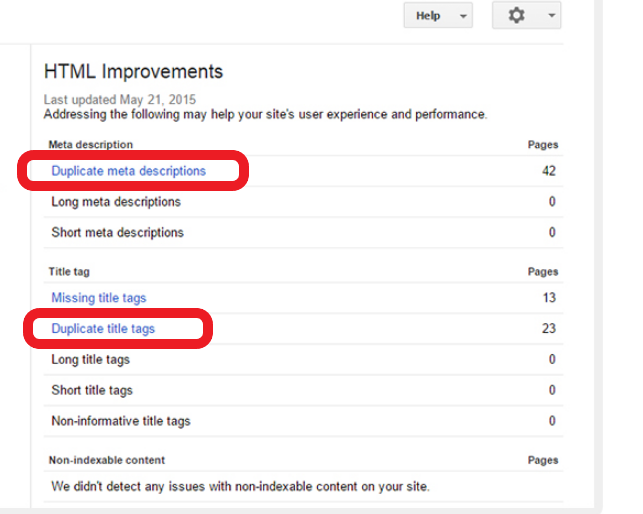
So in fact, according to search system requirements, repeating metadata is opposed to a "useful page" term. Logically, if a page has duplicated information, then it cannot be useful. That is why it should be corrected.
Google describes mistakes like this in its Google Search Console instrument:
These faults will not prevent your website from appearing in the search results, but avoiding them can increase the quantity of page visitors.
You must admit that the statements "it will not prevent your website from appearing in search results" and "it can increase the quantity of page visitors" are quite controversial.
#2
Missing meta-tags
Aside from the situation when a report includes pages that don't need any title (like CMS service pages), this kind of pages should not be open to search systems. But in fact, that's not our subject. Optimally, there must be no pages that do not have Title.
If there are pages that you are not willing to promote, then you should either close them for indexing or use them to the site advantage, which will be discussed in the practical part.
#3
Tags length and information content
This requirement has already been reviewed earlier. Keep it in mind that the optimization of metadata length should not be done to the detriment of informativity.
What is not stated in the official tools:
#1
The absence of ALT and H-type titles
#2
Spam
This irregularity may be detected in any element that we review. We have just given an example of spam in ALT. The same errors were mentioned in the last myth as well. So if we aim to make a spam Title, then it will look like:
"Spanners, and also spanners, buy spanners, spanners in our catalog"
Spam is not recorded anywhere because it can be referred to the errors that are on the optimizer's consistence. Spam will not let your web page appear in the search results; that's why it's important to use only important info instead of spam.
Any recommendations on quantity like "you should only mention the keyword once" or "the query topic must be mentioned only once" are not correct.
Let's think logically and make metadata informative. Possible variants are presented in the practical part.
How to optimize metadata and images of a webpage
Our recommendations are designed like "how you should not do" on purpose. If you define your optimization strategy and get rid of mistakes, errors and myths, you'll manage to complete implementation in a way that is comfortable for you in terms of programming and your business targets.
Here are the headnotes that can help you to strategize and optimize your work:
1. Title and Descriptions implementation
- Divide the pages according to promotion priorities and your business targets. From SEO viewpoint, those are the site pages that become essential by default that have carefully chosen semantics (considering that the semantics was gathered in all pages of the site).
- Apply your mental skill. Divide the pages that do not contain any semantic by type: filter page, product cards, catalog. Make the logic of metadata formation for these pages.
Once we mentioned, off-priority pages should be used to the advantage of your website. I recommend making formulas that generate automatic metadata for each page type using visitors' intentions that are important for your business. Example: "buy", "price", "cost", "order" and the content of your site.
Here is an example of this kind of formula:
| Formula | URL | Example |
|---|---|---|
| H1 pages - buy in New York, low prices. Category name - electrical equipment sales in online catalog of internet electronics store Shop name. | Electrical equipment - buy in New York - good prices for electrical equipment - electrical equipment sales in online electronics store example.ua |
To implement this kind of formula, you should work previously upon H1 headings, as they will be among the variables.
| Formula | URL | Example |
|---|---|---|
| The last breadcrumb meaning | sockets, switches |
You should define which data is going to be variable - no matter it can be breadcrumbs, categories and other. Mind that big text pieces without variables should be avoided to prevent duplicating.
2. Avoid duplication. Delete all the unnecessary information
Within the technical specifications, we indicate an H1 headings formula for pagination pages and their Titles. We recommend you to delete Description from these pages.
| Formula | URL | Example |
|---|---|---|
| The title of the category - page # The pagination page number. | Powers connectors - page #2 |
3. Automate the task to a maximum level
Within such formulas, you can make unique product card names to avoid duplication. If your cards names are like "woman dress" - "woman dress", so probably their duplications will take place.
Add item number to the text of H1 headings in order to make cards unique.
4. Write attractive descriptions
It is hard to escape the conclusion that snippets are not really important. But it is worth noticing that this point of view is not correct. It's essential to follow logic and not to aim for beauty.
That is why it is not recommended to use telephone numbers and addresses in Description. You can use your site and micro markdown for this purpose. Though there is an opportunity to make a call quickly using the number found in the description - it's not any help for analytics.
Don't revolve around Descriptions only. If a search robot uses the content of the whole web page to create a snippet, so why to get obsessed with meta-tags? Implement micro markdowns for this purpose, I will mention this fact one more time. I advise you to add the site name into the headings following the advice of advertising specialists. As we can see in the example above - it is advantageous, especially for brand recognition.
Using " Unicode characters table " and adding a couple of symbols to Description will underline the information that you are willing to highlight.
| Formula | URL | Example |
|---|---|---|
| H1 of the page - delivery to NY, Washington and Chicago category name ⚡ price in online catalog of the Internet shop site name | Electrical equipment with the delivery to NY, Washington and Chicago Electrical equipment⚡ catalog price in the internet shop example.ua |
5. Use unique queries and word forms instead of spam
It concerns formulas and pages of high priority generating. It's better to write Titles for such pages by hand, not filling them up with spam, but using various synonyms. Search engine sees a page as a text.
The text is one of the means that helps to show the usefulness of the page. Which of the following pages is a search engine most likely to prefer:
|
Smartphone Samsung, Samsung smartphone, Samsung telephone |
Samsung smartphone, Samsung telephone, Samsung mobile, cellphone |
Most likely, the robot will prefer the one with the row of synonyms. So be precise working with high priority pages. Use synonyms from your semantic kernel, from search results "clues" or just make the unique word forms up from your head!
6. Shape your CMP
As it was mentioned before, the pages that have not to be indexed should be closed for indexation. But please mind the user and the fact that Title brings a user to your page. That is why it is strongly recommended to implement correct Title both for the 404-page and for the search page of your site.
All visitors should have no trouble with navigation. Having completed the optimization stage, you should not forget about the spelling check-out procedure before the process of implementation, as the factor of human error is always possible.
7. Pay attention to H-headings
Implementation of these kinds of headings is a question of strategy. We follow these rules:
- For each page, there must be one H-heading. Two obligatory aspects you should check - each page should obtain the H-heading, and this one should be unique.
- Don't use H-headings in page making, use the ones that are similar in style.
- Use H-headings in texts minding their structure. If a text heading contains a key query, we recommend to use H2-heading. If there is a general heading, like "About the product", then use H3.
H1 heading made in a correct way will give you all needful capabilities to complete the Title forming stage, while using generating formulas. Here is an example of such task:
| Formula | URL | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Category, “title of constraint box(filter) : The title should be written with a capital letter". | Switches, sockets - Asfora serie. |
8. Image optimization
Useful information can be found in Google recommendations , let's define main headnotes and add some practical examples that may influence your optimization in a positive way:
- Give comprehensive image links.
- Don't spam in ALTs of the pictures, don't use keywords.
- Balance the length of the text, it should belong just enough to take the point further.
- Use unique pictures and high-quality photos.
- Write text behind pictures.
And finally, my personal advice:
- Make ALT and Title unique; for online shopping use generating formulas:
For all news and service pages with several images, it is necessary to implement ALT and Title for second, third and each following picture using this formula:
- Alt of the image: "Page name" - photo № "photo's number".
- Title of the image: "Page name" - photo № "photo's number".
- Make sure that the search robot can reach your pictures and optimize their size. For the right access to the pics, you should configure Robots.txt and Sitemap.xml.
To choose a better way to perform the images to the searching system, you need to realize how these systems work. Here is an example of a Google bot activity. It also works with images, but the work between the main robot and the picture bot is distributed automatically without your interference. As we can see, User-agent Googlebot can be used for pictures, that is why it's just enough to check if your pictures are accessible.
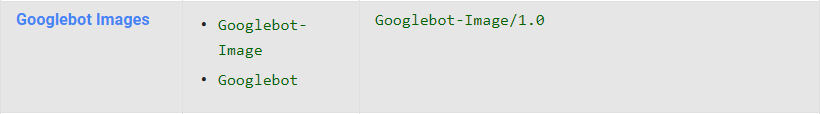
Working with Google, there is an opportunity to create a separate XML site map for pics. Map format is available in references and also may be generated automatically with Screaming Frog Spider or other services. Google makes it possible to form one and the same map for pages and images. The choice is up to you, but if you ask me,
I'll recommend creating different maps for page and image navigation, especially for big websites. Don't forget to add the site map to the scanning tool.
Conclusion
Someone would stay disappointed in this guidance because there are no cases, proofs and working schemes. But it is notable that I did not have a purpose to create such an article. To my mind, metadata and image optimization must be a part of a general SEO-promotion strategy.
It should be based on a range of work in other fields as your business requirements and the targets of the website. That is why the purpose of this article is to help you to avoid mistakes while making up a strategy. So the main headnotes are the following:
- To get the right information use official sources or the ones that take them as a base.
- Don't believe myths, check and experiment, but try not to use your main business for that.
- Use logic and common sense, don't try to cheat on anybody, see search engines as partners and don't break its rules and recommendations.
- Automate work and run the check-out procedure before any implementation process you are planing. It helps you to save time and makes it easier to correct the possible mistakes.
