No wonder fixing duplication issues is one of the most important aspects of site optimization.
Webmasters often use a 301 redirect as a method of solving this problem, however, it's not always an option. That's where the canonical tag comes into play.
Not using this simple way of fixing the (inevitable) issue of duplicate content on your website, and therefore, boosting your SEO efficiency, would almost be a crime.
So let's get straight to the point and answer all the most common questions.
What is a canonical tag
What are canonical pages
If the website includes pages with duplicate content, only one of them will be shown. If you don't specify it yourself, it will be randomly selected by the robot. The term "canonical" refers to this specific type of page, the one that ends up appearing in search results.
By using the link rel="canonical" attribute, you're giving an instruction to search engine robots, which of the duplicate pages is preferred, and supposed to be canonical, rather than allowing them to pick it randomly.
How does rel="canonical" work
The canonical tag is a signal for search engines to start considering the page's priority. It can be placed on any HTML-page between the <head> and </head> tags.
When there are identical or extremely similar pieces of content under different URLs on your website, using the canonical tag will mark the master page, which will be the one shown to search engines.
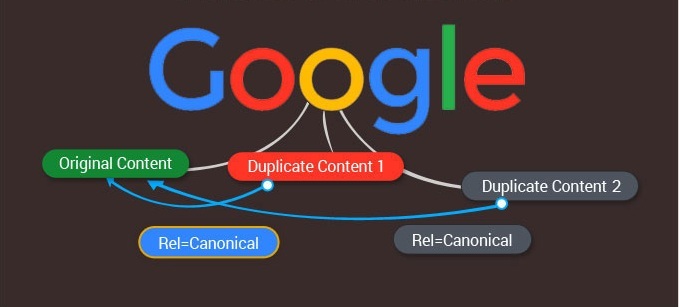
Canonical tags vs 301 redirects
What is definitely going to complement your SEO strategy? The answer is simple: you should always redirect when it's needed. However, in some cases it isn't always the best and easiest way to go, for the following reasons:
- its time-consuming realization process;
- some pages are regularly used by visitors
In this case, you should certainly set a canonical URL if you don't want to get in trouble with the search robots.
Advantages of the rel="canonical" for SEO
Search engine robots have a very negative attitude to the content they deem duplicate. They refuse to index identical text, whether it comes from different websites, or from pages within the same domain. Solving this issue is an essential aspect of an effective internal site optimization.
Making the content noticeable for users leads to an increase in visits and positively influences the site's conversion. A canonical URL can also refer to another domain if the content on these pages is the same.
How exactly do you set up rel="canonical"
Canonical URLs can be specified by using different methods. We want to introduce the best ways for canonicalization, keeping things simple and organized:
#1 On the page: HTML tag (rel=canonical)
The easiest and most obvious way to specify canonical pages is pasting the rel="canonical" attribute into the code of the page. Just insert the piece of code into any duplicate page's <head> section.
<link rel="canonical" href="http://your-website.com/canonical-page.html"/>
Keep in mind: The tag must be placed in <head> </head> section. If you accidentally set the tag someplace else, it will simply be ignored by the search engines
#2 HTTP header
There is no <head> section in some documents, so it's impossible to place canonical tags in the page header. To set canonicals in such instances, you'll need to use HTTP headers. On ordinary webpages, you may also implement a canonical in HTTP headers.
#3 XML-sitemap
Sitemap is also a great way to point search robots at the pages on your website that are the most essential. Sitemap URLs are a simple approach to define canonicals for a large website.However, there is a slight chance that search engines could ignore the tag.
#4 Server's response
This option is suitable for non-HTML formats. For instance, if you need to index a PDF-document, you can add the rel="canonical" attribute to the http. In this case, the server will show the following thing:
Link: <http://your-website.com/main-file.pdf>; rel="canonical"
The only issue is that Google currently supports <link> element for web search only.
The main mistakes of using rel="canonical"
1. rel="canonical" is used for the first page of a pagination series
A website's article can consist of many pages. Since the second, third, and all subsequent pages of the article are not duplicates, using the rel=canonical attribute to designate the first page as canonical would be erroneous. In this situation, a search engine error will prevent pages 2 and 3 from being indexed altogether.
2. Absolute URLs are mistakenly taken for relative
Absolute URLs require the full address, including http://. If a webmaster mistakenly puts example.com/shoes.html instead of http://example.com/example.com/shoes.html, search engines may ignore the rel=canonical tag.
3. Unintentional use of rel="canonical", attribute use on multiple pages
When webmasters replicate the page template, they often forget to modify the attribute. These errors are accidental, but they may lead to severe negative repercussions.
4. A page section links to a specific article
If you have numerous areas on your website where you publish several articles daily, the content of the section page is identical to that of the article page. To eliminate duplicates, use rel="canonical" to make the article page the canonical version. In this case, it is advisable not to set attributes at all, since the search engine will not display a page with a section in the results.
5. rel="canonical" is used in body
The rel="canonical" attribute should only be included in a head section of an HTML document. If it falls into the body section, search engines tend to ignore it.
Rules for specifying canonical links
As you can see, when using canonical links, webmasters can make plenty of mistakes, which could cause serious problems and traffic loss. To avoid them, you have to follow these rules:
- One page — one rel="canonical" tag in <head> section.
- Make sure that the tagged page has been indexed.
- Don't complicate the link structure by building chains of canonical URLs.
- If you tag a page using several methods, be sure that all the links refer to the same page.
- Choose absolute links instead of relative ones. It will minimize errors and prevent search engines from ignoring the pages:
- Wrong: <link rel="canonical" href="shop.com/tables.html" />
- Correct: <link rel="canonical" href="http://shop.com/tables.html" />
Correct examples of using rel="canonical"
Despite it being a quite useful tag, using isn't always reasonable. There are several particular cases when the canonical pages are definitely needed:
#1 Search in online-shops
Canonical is a must when it comes to the search catalog in an online store.
Let's illustrate it with an example: different people find the same goods by using various search methods. Person 1 is looking for a pair of shoes by choosing the brand or model. At the same time, Person 2 finds the same list of shoes via setting a particular price range or rating. Both of them land on pages with the same content, but the page URLs are actually different.
To solve it, just pick one main page, and refer all the other ones to it, simply by tagging them with the canonical attribute.
<link rel="canonical" href="http://online-shop.com/tables.html"/>
#2 Several goods of the one type
This situation is also related to online stores.For instance, you might have a list of practically same goods, only differing by color. It is better to choose one of them as canonical and bind other ones to it, otherwise the bots will consider such pages to be duplicate content.
#3 Loyalty program for clients
If there is a loyalty system on your site which includes bonuses, discounts, and special offers for frequent customers, create links with rel="canonical" on pages for special clients and direct them to the standard ones.
#4 Pages of pagination
Pagination creates duplicate content. If there is a «View all» page on your site, refer all the connected URLs to it.
#5 Work with the UTM
If you use the UTM to monitor the efficiency of your advertisement campaign, you need to remove doubles. Place the canonical link from the page with the UTM to to the basic page.
Sometimes it's pretty hard to understand what page should be considered the main one. The page has to be the most suitable for indexation. In order to make the right choice, it is better to look at these two aspects:
- page traffic;
- the number of the internal/external links.
Conclusion
With help of the rel="canonical" tag, you can manage content duplication on your website and show search engines what pages are should be indexed. The reasonable use of this instrument positively influences the site's indexing, ranking, traffic and conversion as a result.
As we've discussed, there are several methods of adjusting the canonicalization. Choose the most suitable one for you, and pay attention to details in order to use the tag properly and avoid the most common mistakes.
