Using <input type="password"> in data input forms on websites
The password input element <input type="password"> is designed to register users on websites. Normally, the text typed in by the user in this field is replaced for security reasons with special characters: stars or dots.
On mobile devices, the entered character is usually shown for a second so that the user can verify that the text typed on a small virtual keyboard is correct.
In this field, you can add an identifier or a name:
<input id="Pass_of_user" type="password">
<input type="password" name="my_password">
There are the following options of unprotected use of user data:
Protecting user data using HTTPS
Due to the insecurity of the HTTP protocol, you must use HTTPS on any websites that utilize user data. This protocol is designed to protect users' personal data from interception and modification.
Browsers display warnings about the insecure connection to inform users of a potential threat on websites using the HTTP protocol. In Google Chrome, there is a more forceful wording:
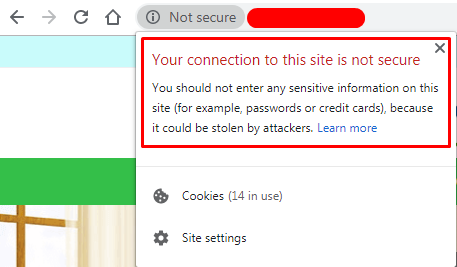
One survey found that nearly half of users have a bad reaction to 'not secure' browser warning. However, 46% of respondents said that they would not enter their names or financial information into a website that was not secure, and 64% of survey participants said they would leave the website "instantly".
Resource insecurity warnings can also affect brand reputation. Given the aggregate evidence that the HTTPS protocol is a ranking factor and the impact of browser warnings on visitor behavior, experts unequivocally recommend switching to a secure protocol.
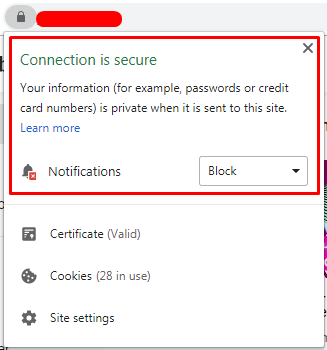
You must use an SSL certificate in order for the website not to have a message that scares potential customers; in that case, a browser message will inform you about the website's security:
Why is it important to ensure the safety of users' personal data on all websites
There are situations when news and entertainment websites where visitors do not enter confidential and financial information do not treat storing data about usernames and passwords responsibly. In this case, there is a high threat to user security who use the same sets of logins and passwords on several websites.
Hackers can attack a news portal, obtain passwords and logins, and then use them on other websites containing important financial information, for example, online banking services. Accordingly, ensuring the security of personal data depends not only on the competent actions of website developers but also on the users themselves.
There are certain rules for using passwords that will minimize the risk of identity theft. Some data protection guidelines apply to website owners, others apply to users.
Recommendations for administrators:
The password entered by a user must be checked for compliance with these requirements.
For example, if you type your password incorrectly three times, your account can be blocked for several minutes or longer. This will greatly complicate hacker attacks with password guessing.
Therefore, by inviting users to change passwords every 60 or 90 days, it is possible to ensure the safe storage of their personal data.
Otherwise, there is a risk of being hacked by the automated password guessing (brute force) software.
- it is advisable to use meaningless combinations of letters and symbols that are not related to personal information;
- passwords for different websites should be different. If you cannot remember them, you can use password managers. However, in this case, you must carefully select a complex password for this tool.
You can install LastPass: Free Password Manager that allows storing passwords, addresses, and other data securely for auto-filling forms:
Conclusion
- The security of transferring and storing user data is one of the priorities in the operation of any website.
- You can protect your personal data using the HTTPS protocol.
- It is important to monitor the strength of passwords entered by users by adding appropriate checks and recommendations.
- It is useful to regularly suggest changing the password in user accounts to mitigate the risk of cracking them.
- Administrator passwords should be as complex as possible, you must remember to change them as often as possible.
